Transforming Your Life with Your Own Cells
In the journey of battling serious illnesses, especially those like certain cancers, the medical field has offered hope through advanced treatments. One such treatment is the autologous Cell therapy, a procedure that has been a game-changer for many patients. This innovative treatment utilizes a patient’s own Cells to potentially repair damaged tissues and promote healing. This blog aims to demystify the process, explain how it differs from other types of Cell transplants, and offer insights into the risks, benefits, and recovery process.
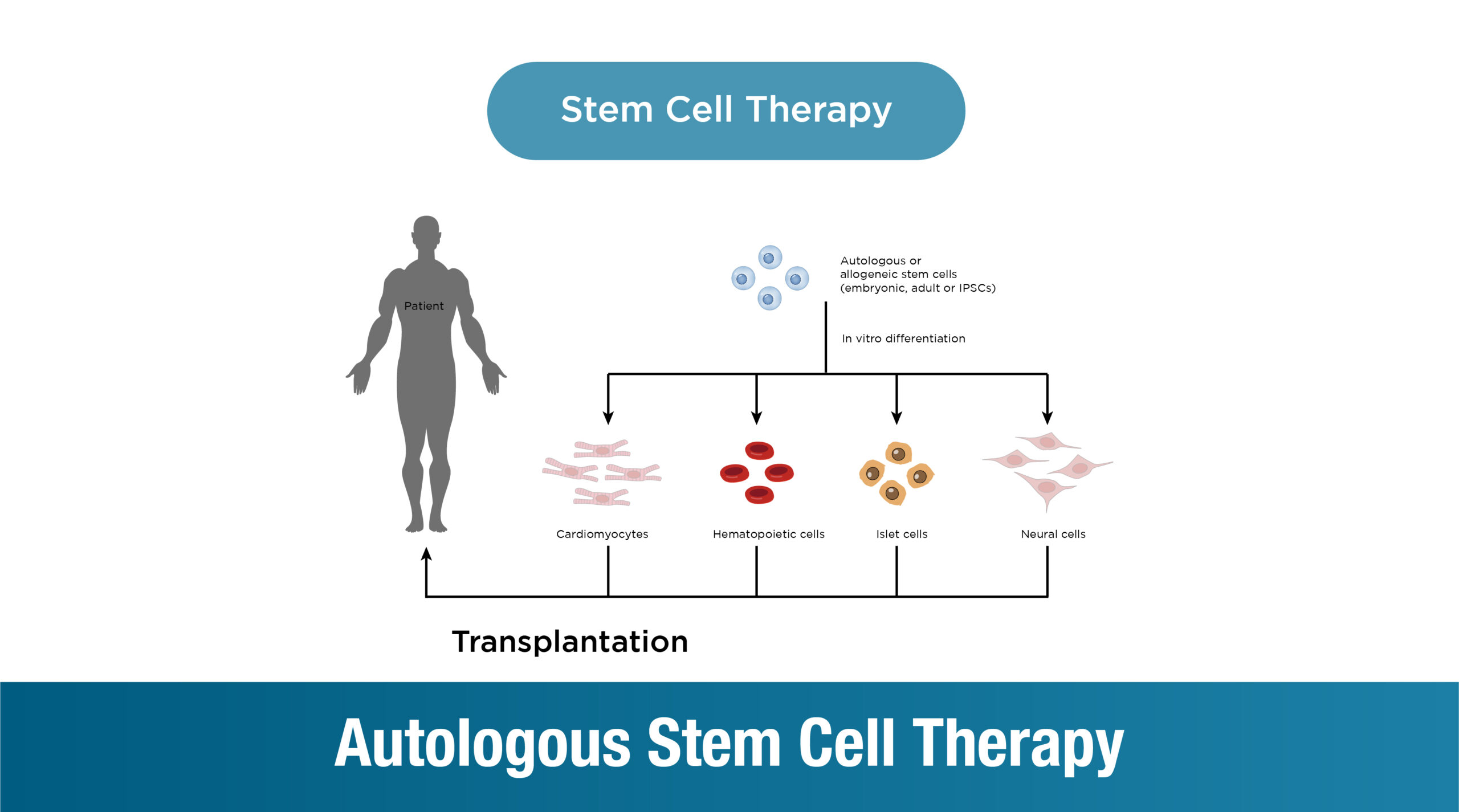
What is Autologous Cell Therapy?
Autologous Cell therapy involves collecting and using a patient’s own Cells to treat a variety of conditions. Cells are the body’s raw materials—cells that can develop into many different types of cells and tissues. In this therapy, these cells are harvested, processed, and reintroduced into the patient’s body to aid in the regeneration of damaged tissues and improve overall function.
Unlike Cell transplantation, which involves different types of Cells from various sources, autologous Cell therapy uses cells sourced directly from the patient, thereby reducing the risk of complications related to donor cells.
How Does Autologous Cell Therapy Differ from Cell Transplantation?
While the terms autologous Cell therapy and “autologous Cell transplantation” are sometimes used interchangeably, they refer to distinct procedures.
- Autologous Cell Therapy: Utilizes the patient’s own Cells to repair or regenerate damaged tissues. This approach minimizes the risk of immune rejection and complications associated with donor cells.
- Cell Transplantation: Involves the introduction of Cells into the patient’s body, which can be either autologous (from the patient) or allogeneic (from a donor). The focus here is often on replacing damaged or diseased cells rather than repairing them.
Steps Involved in Autologous Cell Therapy
- Cell Collection: The process begins with collecting Cells from the patient’s blood or bone marrow. This is often done through a procedure known as apheresis, where blood is drawn, the Cells are separated, and the remaining blood is returned to the patient.
- Processing and Preparation: The collected Cells are processed and prepared for reintroduction. This step may involve expanding the number of Cells or concentrating specific types of cells needed for therapy.
- Reintroduction: The processed Cells are then reintroduced into the patient’s body, typically through an intravenous infusion. These cells migrate to the damaged areas, where they begin the process of tissue repair and regeneration.
- Recovery and Monitoring: Post-therapy, the patient undergoes a period of recovery where the new cells begin to integrate and function. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor progress and address any potential issues.
Eligibility Criteria for Autologous Cell Therapy
The eligibility criteria for an autologous Cell therapy typically includes:
- Age and Overall Health: Younger patients and those in good health, aside from their underlying condition, are generally better candidates.
- Disease Status: The disease must be in partial or complete remission before the transplant can take place. The patient’s medical team will assess the risk versus benefit of proceeding with the transplant.
- Organ Function: Heart, lung, liver, and kidney functions must be within acceptable limits. A comprehensive evaluation is conducted to ensure the patient can withstand the rigors of the transplant process.
Risks and Benefits of Autologous Cell Therapy
Autologous Cell therapycomes with both risks and benefits. Understanding these can help patients make an informed decision.
Benefits:
- Reduced Risk of Immune Rejection: Since the therapy uses the patient’s own cells, the risk of rejection is minimal.
- No Need for Donor Matching: Eliminates the need to find a compatible donor, simplifying the process and potentially speeding up treatment.
- Personalized Treatment: Tailored to the patient’s specific needs, enhancing the potential for positive outcomes.
Risks:
- Limited Effectiveness: The success of the therapy can vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual’s response.
- Potential Side Effects: As with any medical procedure, there may be side effects, including localized pain or discomfort at the injection site.
Recovery Process and Aftercare
Recovery from autologous Cell therapy typically involves:
- Immediate Recovery: Patients may experience some initial discomfort or side effects, but recovery is generally manageable with appropriate care.
- Long-Term Recovery: Ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are essential. Patients may need time to see the full benefits of the therapy and to adapt to any changes.
Aftercare: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and avoiding infections, supports the healing process. Emotional and psychological support can also play a crucial role in recovery.
Autologous Cell Therapy at Plexus Neuro and Cell Research Center
Autologous Cell therapy represents a powerful tool in the fight against certain cancers and other serious diseases. At Plexus Neuro and Cell Research Center, located in Bangalore and Hyderabad, we are pioneers in autologous Cell therapy. Led by Dr. Na’eem Sadiq, we specialize in treating complex neurological and autoimmune disorders such as cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries. What truly distinguishes us is our unique approach of integrating Cell therapy with personalized neuro-rehabilitation, providing our patients with a comprehensive, holistic path to recovery.
We believe in combining cutting-edge technology with compassionate care to achieve remarkable outcomes. Our personalized treatment plans are crafted to meet the specific needs of each patient, ensuring not just immediate relief but also long-term enhancements in quality of life. With our state-of-the-art facilities and a dedicated team of experts, we are committed to delivering the highest standards of care.
Diseases Treated with Autologous Cell Therapy at Plexus
Autologous Cell therapy also offers promising treatment options for various neurological disorders. At Plexus Neuro and Cell Research Center, we use this innovative approach to address a range of conditions, including:
- Cerebral Palsy: Autologous Cell therapy can help improve motor function and reduce the severity of symptoms. By promoting neural repair and regeneration, our treatment aims to enhance overall quality of life and support better physical outcomes.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Our Cell therapy is designed to modulate the immune system and promote the repair of damaged nerve tissues. This can potentially slow disease progression, improve neurological function, and offer relief from symptoms.
- Spinal Cord Injuries: Autologous Cell therapy supports nerve regeneration and promotes repairs in spinal cord injuries. Our approach focuses on enhancing functional recovery and improving motor and sensory abilities, offering hope for better mobility and quality of life.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders: For conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, Cell therapy at Plexus aims to address underlying neurodegeneration and promote brain cell regeneration. This can potentially help manage symptoms and improve cognitive and motor functions.
If you or a loved one is considering this treatment, understanding the process, risks, and benefits is the first step toward making an informed decision. Remember, you’re not alone on this journey—support is available every step of the way.
Reach out to our centers in Bangalore and Hyderabad today.
WhatsApp +91 89048 42087
Call +91 78159 64668 (Hyderabad) | +91 82299 99888 (Bangalore)
FAQs
What are the 3 types of Cell transplants?
The three types of Cell transplants are:
- Autologous: Uses the patient’s own Cells.
- Allogeneic: Uses Cells from a donor with a compatible tissue type.
- Syngeneic: Uses Cells from an identical twin.
What is the difference between autologous and allogeneic Cell therapy?
- Autologous: Utilizes the patient’s own Cells, reducing the risk of rejection.
- Allogeneic: Involves Cells from a donor, which may require immunosuppression to prevent graft-versus-host disease.
What is the success rate of autologous Cell therapy?
The success rate varies by condition but generally ranges from 40% to 70% for cancers like multiple myeloma and lymphoma, with higher rates for some diseases and lower for others. For neurological disorders, the success rate of autologous Cell therapy varies widely based on the specific condition and the stage of the disease.
- Cerebral Palsy: Improvements in motor function and quality of life have been observed in many cases.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Early studies show potential for slowing disease progression and improving symptoms.
- Spinal Cord Injuries: Some patients experience significant improvements in motor and sensory functions, but success rates depend on the severity of the injury and timing of the transplant.
Can you live a normal life after Cell therapy?
Yes, you can return to a normal life post-transplant, though recovery can be gradual. Long-term health depends on the disease, treatment success, and any potential side effects or complications.
What is the recovery time for autologous Cell therapy procedure?
Recovery typically takes 3 to 6 months. Initial recovery involves a hospital stay of 2 to 4 weeks, with gradual return to normal activities as the immune system rebuilds and side effects diminish.










