Brachial plexus injuries significantly impact the function and mobility of the upper limbs, posing challenges for both adults and infants. Through this comprehensive guide, let’s talk about brachial plexus injury exercises, as well as cover a range of treatments and therapies designed to promote recovery. From targeted exercises for infants to weight-bearing strategies, there are several physiotherapist and occupational therapist recommended exercises that can enhance strength, flexibility, and overall functionality.
Understanding Brachial Plexus Injury
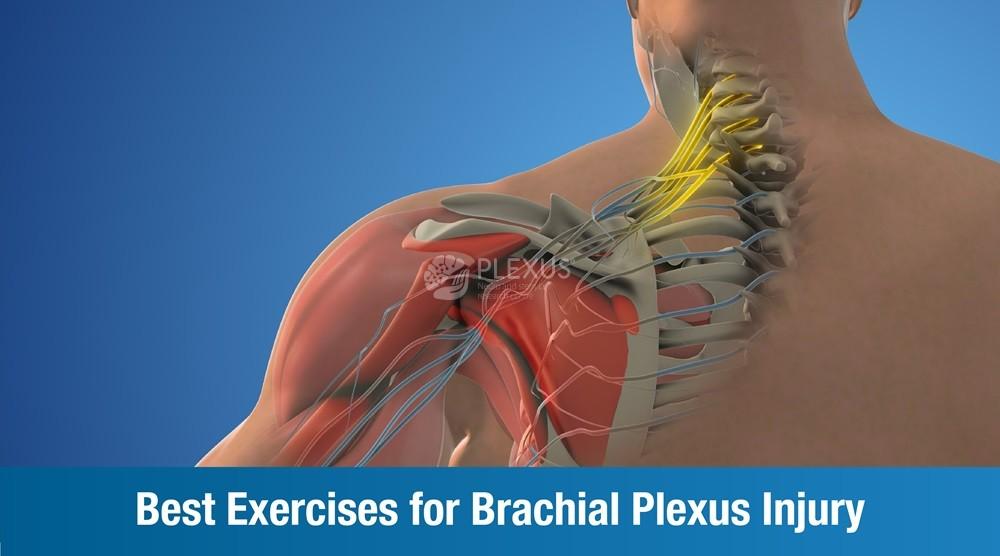
A brachial plexus injury (BPI) is a condition that involves damage to the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that control the muscles of the shoulder, arm, and hand. It is a complex network of nerves that originates from the spinal cord in the neck and extends down the arm.
Typically, brachial plexus injuries occur during childbirth, particularly when there is difficulty delivering the baby’s shoulder. This can happen in cases of shoulder dystocia, where the baby’s head has passed through the birth canal, but the shoulders become stuck behind the mother’s pelvic bone. The stretching or tearing of the brachial plexus nerves during these situations can lead to injury.
The most common symptoms include:
- Weakness or paralysis in the affected arm: The severity can range from mild weakness to complete loss of movement.
- Loss of sensation: The affected arm may experience reduced or loss of sensation.
- Impaired reflexes: Reflexes in the affected arm may be diminished.
The treatment for brachial plexus injuries involves a routine of exercises customized to the individual’s specific condition. From gentle stretches to progressive strengthening routines, these exercises play a crucial role in restoring function and reducing long-term complications.
Brachial Plexus Injury Infant Exercises
Exercises for infants with brachial plexus injuries generally involve a gentle range of motion exercises to start with. This routine can gradually include facilitated stretching, and playful activities that can stimulate nerve and muscle growth. Below are some of the most common infant exercises for brachial plexus injury:\
Passive range of motion (PROM) exercises
- Gently move the infant’s affected arm through its range of motion.
- Hold the infant’s hand and guide the arm in different directions – flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
- Stick to a gentle daily rhythm for these exercises to prevent stiffness.
Gentle stretching
- Gently extend and flex the infant’s wrist, elbow and fingers.
- Do not force the joints into uncomfortable positions.
- Routine stretching will prevent contractures.
Tummy time
- Place the infant on their bellies for short periods.
This can be done as early as when the baby is just a week old
- Make sure you supervise all the time, and the baby is comfortable during tummy time.
- When done regularly and correctly, tummy time helps strengthen the muscles in the neck, shoulders, and arms.
Mirror therapy
- With the help of a mirror, create a reflection of the infant’s unaffected arm, making it appear as if the affected arm is moving.
- This helps stimulate movement and coordination in the affected arm.
Weight-bearing exercises
- Create obstacle courses with sofa cushions and bolsters to encourage crawling.
- Place toys a little out of reach to motivate the baby to reach for the toys while using the affected arm.
Gross motor activities
- Encourage reaching and grabbing through engaging play.
- Use colorful blocks, stacking cups, peg dolls, etc to motivate the baby to use the affected arm.
Massage
- Soothing and relaxing, gentle massages promote circulation and relaxation.
- When massaging a baby, especially an infant, make sure you use only gentle strokes and are mindful of the baby’s comfort. DO NOT pull or apply pressure on the joints and limbs. It does not benefit the baby.
When performing these exercises it is important to adopt a gentle approach. Infants and babies are delicate. At Plexus, we use a combination of physical therapy and occupational therapy to devise a set of exercises aimed at improving muscle strength, joint flexibility, and overall functionality. Depending on the severity of the child’s symptoms we also perform nerve gliding exercises, resistance training, proprioceptive (balance) activities.
We also help parents and caregivers create supportive and nurturing environments at home to facilitate natural movement patterns, promote muscle development, and improve motor coordination.
Brachial Plexus Injury Adult Exercises
Although rare, adults can also sustain brachial plexus injuries while performing simple everyday activities. At Plexus, we use a combination of the below exercises to help support movement and coordination.
Lateral raises (with dumbbells)
- Stand up straight
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together
- Holding a dumbbell in your right hand, turn the thumb upwards, towards the ceiling
- Lift your right arm out to the side, making it parallel to the floor
- Hold for five counts, lower the arm
- Repeat motion with other hand
- Do 5 sets twice a day
Biceps curls (with dumbbells)
- Holding a dumbbell in one hand, keep your arm straight, resting by your side
- Gently bend your elbow as much as you can, bringing your dumbbell plate up
- Hold for five counts
- Release, bring arm down to the side
- Repeat eight to ten counts
Wrist curls (with dumbbells)
- Leaning forward and rest your forearm (holding the dumbbell) on your thigh
- Stabilize your arm by placing your other hand on top of your forearm
- Without your forearm leaving your thigh, lift your wrist as much as possible
- Hold for five counts, then lower back down
- Repeat eight to ten counts
Triceps kickbacks (with a bench)
- With a dumbbell in one hand, kneel on a bench with the opposite leg
- Bend forward and place your arm on the bench to support your body weight
- Your wrist should be in line with your shoulder
- Lift your affected arm until your upper arm is parallel to the ground
- Slowly straighten your elbow
- Hold for five counts and lower your arm
- Repeat eight to ten counts
For grip strengthening we recommend using a stress ball – squeeze for 45-60 seconds, release and repeat. You can do this as often as you can throughout the day.
Rubber band stretches also help improve finger dexterity – wrap a rubber band around your fingers (not thumb), spread your fingers, and hold for 8-10 seconds, slowly join your fingers together; repeat as often as you can.
Performing everyday activities, such as dressing, eating, combing your hair, putting on makeup, etc can help improve everyday functionality.
Brachial Plexus Injury Rehabilitation at Plexus
The above exercises have been specially recommended by our team of expert physical and occupational therapists. They are a key component of Plexus’ brachial plexus injury rehabilitation.
At Plexus, our treatment program for brachial plexus injury takes into account the severity of the injury, the nerves affected, as well as the patient’s overall health. Our centres in Bangalore and Hyderabad offer regenerative rehabilitation program for brachial plexus injury that comprises a combination of:
- Stem cell therapy: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) help in the repair of torn nerve roots
- Physiotherapy: This involves range of motion exercises, stretching, and strength training
- Occupational therapy: Here, the focus is on fine motor skill development and activities for daily living (ADL) training.
Physical and occupational therapy are crucial for maximizing function and preventing complications.
- Splinting and bracing: In very rare cases, splints and braces are used to maintain alignment, support the affected arm, as well as prevent contractures.
- Patient and caregiver counseling: This includes support services to address the psychological and emotional impact of coping with a brachial plexus injury.
While we do believe the above treatment approaches are the most effective, there are rare cases that present significant nerve damage. For these, we recommend nerve surgery that typically involves nerve grafts or transfers so as to repair damaged nerves, and promote healthy nerve function.
FAQs
How do you rehab a brachial plexus injury?
Plexus’ brachial plexus rehabilitation involves a multidisciplinary approach that includes stem cell therapy, assisted devices (in rare cases), physical therapy, occupational therapy, and exercises targeting muscle strength and flexibility. Consistent rehabilitation is vital for restoring range of motion, strength, and overall functionality in affected limbs.
What is the best treatment for brachial plexus?
In most cases, the best treatment for brachial plexus injuries often involves a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy. Surgical intervention may be required only in rare and severe cases. The key to maximising functional recovery is timely and comprehensive rehabilitation.
What vitamins are good for the brachial plexus?
Vitamins such as B6 and B12 contribute to the overall nerve health. These vitamins support nerve function, repair, and regeneration. Adequate levels of vitamin D are also beneficial for bone health, which indirectly impacts the brachial plexus. We recommend consulting your doctor before starting on any supplements.
What should you avoid with a brachial plexus injury?
Individuals with a brachial plexus injury should avoid activities that put excessive strain on the affected arm. Heavy lifting, repetitive overhead motions, and extreme stretching can exacerbate symptoms. Maintaining proper posture and avoiding prolonged pressure on the affected limb can go a long way in preventing complications, and aid in the healing process.
Is brachial plexus injury permanent?
This depends on the extent of nerve damage sustained. While some injuries may fully recover with rehabilitation, there are severe cases that may lead to persistent symptoms. Early intervention and rehabilitation increase the chances of significant improvement. However, the speed and extent of improvement also varies from person to person.










